Didanosine: What You Need to Know About This HIV Medication
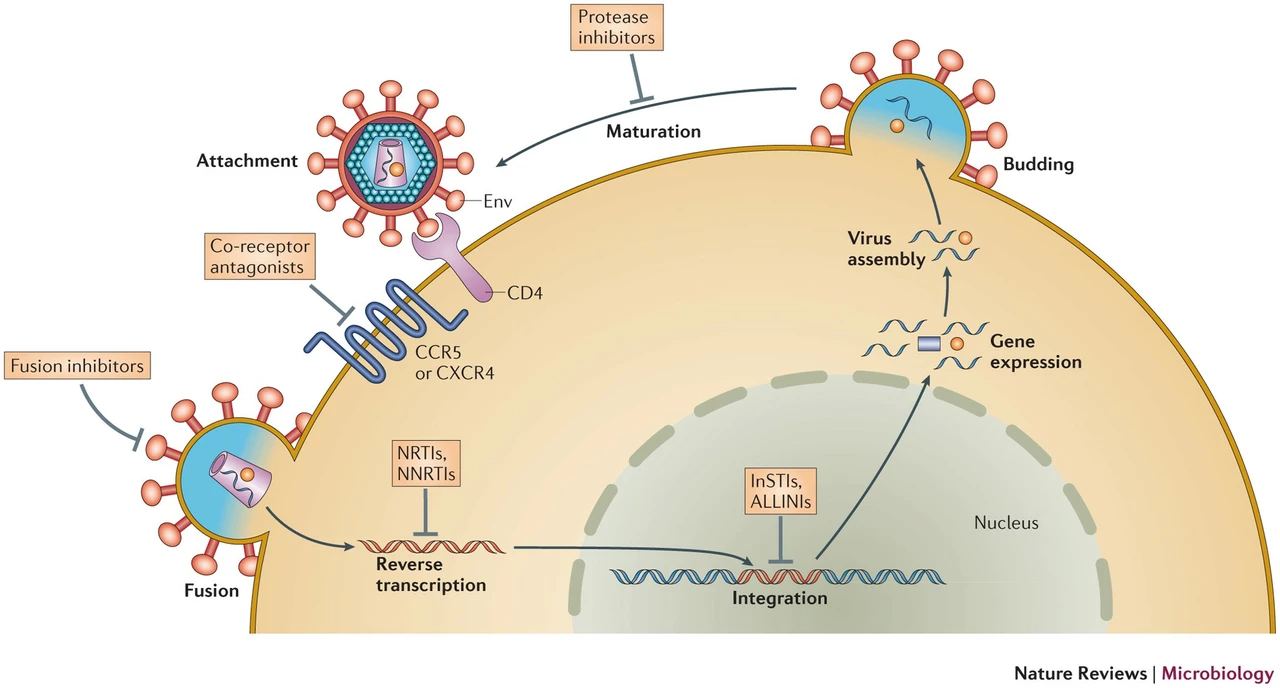
Didanosine is a medication mainly used for treating HIV infection. It belongs to a group of drugs called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), which work by stopping the virus from multiplying inside the body. This helps lower the amount of HIV in your blood and keeps your immune system stronger.
People usually take didanosine alongside other antiretroviral drugs to enhance its effectiveness. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully because missing doses can let the virus grow and become resistant to the medication.
How Didanosine Works and What to Expect
The drug targets an enzyme HIV needs to copy itself. By blocking this enzyme, didanosine slows down the virus's ability to spread. This can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life for those living with HIV.
Didanosine comes in tablet or powder form, which you should take on an empty stomach for better absorption. Drinking water with your dose and avoiding antacids or dairy products at the same time can help prevent stomach issues. If you find dosing times tricky, try setting reminders or linking it to daily routines like brushing your teeth.
Possible Side Effects and Safety Tips
Like all medications, didanosine can cause side effects. Some people might experience nausea, diarrhea, or stomach pain. More serious issues include nerve problems like numbness or tingling in hands and feet. If you notice unusual symptoms, especially muscle weakness or severe stomach pain, contact your healthcare provider right away.
It’s also important to mention any other medications or supplements you’re taking, as didanosine can interact with several of them. Alcohol and certain drugs can increase the risk of liver damage or other complications. Keeping your doctor updated ensures your treatment stays safe and effective.
Didanosine isn't suitable for everyone, especially people with certain liver or pancreas problems. Regular check-ups and blood tests will help track how well the medication is working and spot any early warning signs of trouble.
In short, didanosine plays a vital role in managing HIV when used correctly. Understanding how to take it, watching for side effects, and staying in close contact with your doctor makes a big difference in staying healthy. If you have questions or concerns about this treatment, don’t hesitate to reach out for support.
The role of didanosine in managing HIV-related lung disorders
As a blogger, I recently came across the important role of didanosine in managing HIV-related lung disorders. Didanosine, an antiretroviral medication, has proven to be quite effective in controlling the replication of HIV, thus preventing its progression into AIDS. Consequently, this has helped in reducing the risk of developing lung disorders, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, often associated with HIV. The drug has also been found to enhance the overall immune system, which further aids in combating these lung issues. It's truly fascinating to see how didanosine continues to play a crucial part in improving the lives of those living with HIV.